Robotics in Medicine: Will your future doctor be a robot? Find out!
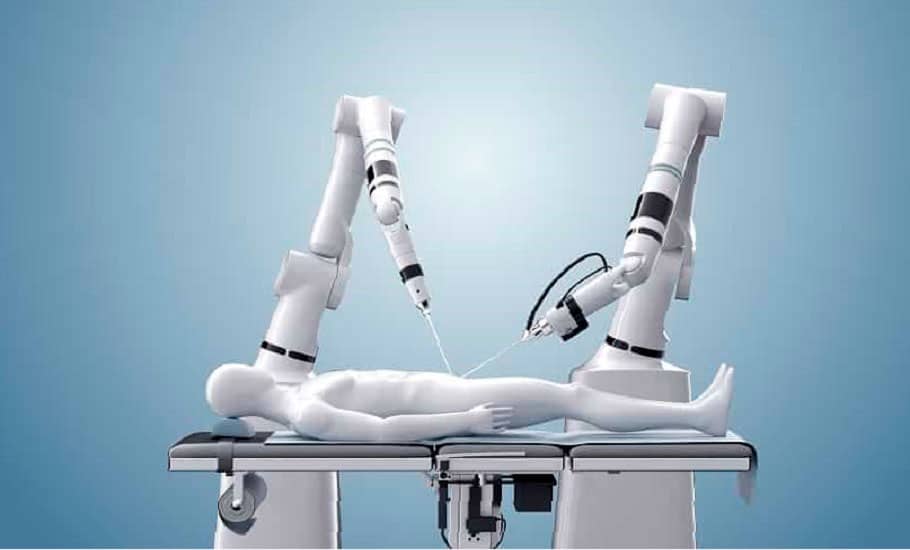
Medical robotics, a type of service robots, leads modern surgeries with its precision and autonomy, revolutionizing healthcare. These autonomous robots perform tasks with pinpoint accuracy, surpassing human limitations. From cardiology to neurosurgery, his impact is undeniable.
Medical robotics is a subfield of robotics that makes heavy use of robots and automation to improve efficiency and precision in the field of healthcare. This technology helps streamline medical procedures, while reducing the workload and hazards for healthcare professionals.
Medical services robots have the ability to operate autonomously or semi-autonomously to carry out different tasks that benefit the well-being of patients. Activities they may perform include intricate surgeries such as heart, gastrointestinal, pediatric, and neurosurgery. The precision and ability of these robots to carry out tasks that are extremely difficult or even impossible for humans due to physical limitations make them particularly useful.
Read on to find out how medical robotics is changing the current medical landscape and how robotic instruments are being used to help surgeons perform ultra-precise surgeries.
Medical robotics components
It is made up of three key elements:
1. Command Post: This is where the surgeon operates the robot using a joystick-like device and monitors the operation through screens that display images and other important data.
2. The automated operating room: This is the physical space where the robot and a set of sensors that provide information to the surgeon are located.
3. The communication network: This network links the command post and the automated operating room, allowing real-time control and interaction.
Medical robots can be grouped into various categories such as surgical assist robots, modular robots, and autonomous robots. In addition to improving patient care and outcomes, these robots also increase operational efficiency in healthcare environments.
Uses and applications
In addition to their use in the operating room, robots are also used in clinical settings to support healthcare workers and enhance patient care. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, robots have been deployed for a wide variety of tasks to help minimize exposure to pathogens.
For example, the Modus V robot is fully automated and even receives commands with voice recognition.
There are also bionic limbs used to help paralyzed patients get up and walk around again. It is an exciting time to be in the field of robotics engineering as these medical robots continue to improve.
Robotics specialists have set their sights on the medical field. Many think that an autonomous robot could soon be a regular member of the medical staff at any hospital, performing all manner of tasks such as taking a patient's vital signs, reading case notes, or even performing surgery!

History of Robotics in Medicine
Robotics in medicine has undergone rapid development since its inception in the second half of the 20th century. With the creation of increasingly sophisticated devices and systems, it has transformed the way many medical and surgical interventions are performed, enabling less invasive and more precise procedures.
First Steps in Medical Robotics
Arthrobot was the first surgical robot created in 1983 and was used as a support by Canadian doctors. After that, other robots were used to perform eye surgeries and later prostate surgeries. These developments came slowly at first throughout the 1980s. In the beginning, the surgeries were carried out by surgeons with precision using the robot in the same operating room. However, modern technology now makes it possible for surgeons to operate remotely.
The early years of robotics in healthcare were characterized by the development of pioneering devices and techniques that paved the way for future advances. Some of the most significant milestones include:
- Creation of the PUMA 560: In 1985, the PUMA 560 robot was used in a brain biopsy, marking the first time a robot was used in a surgical procedure.
- Development of the ROBODOC: In 1992, the ROBODOC was the first robot approved by the FDA to perform hip surgeries.
- Emergence of the Da Vinci Surgical System: In 2000, the FDA approved the Da Vinci Surgical System, a teleoperation-assisted surgical robot that has revolutionized minimally invasive surgery.
In the following decade, in 1990, the AESOP system became the first robot applied to medicine, being approved by the FDA (North American regulation that regulates the use of food, as well as drugs, medical equipment, among others). .
One of the most advanced robots in use today is the da Vinci Surgical System (more details below).
Recent Advances in Medical Robotics
Medical robotics has continued to evolve into the 21st century, with a number of important developments and breakthroughs.
- Telepresence robots: These robots allow doctors to interact with patients remotely, providing medical care in remote or hard-to-reach areas.
- Autonomous surgical robots: Although still in the development and testing stages, autonomous surgical robots promise to perform procedures with a precision and consistency that exceeds human capabilities.
- Rehabilitation robots: Rehabilitation robots help patients regain function and mobility after injury or illness, customizing treatments for each patient's individual needs.
Robotics in medicine continues to be a rapidly growing and evolving field, with the potential to further transform healthcare in the coming decades.
7 Robots in medicine
There are different types of medical robots , designed for the development of various tasks. Next we will see the 7 examples of medical robots:
1. da Vinci Surgical System
It is an extremely precise tool that has been used for more than ten years.

Surgeons can move the microscope during a surgical operation, simply by moving the robot or directing it to move through its software on the computer.
2. Bone cuts – CARLO system

3. MODUS V Robotic Microscope
4. Packaging of medical devices
Just as robots pack and transport boxes in other industries such as manufacturing, they have already taken place in the automation of medical equipment packaging.
5. Kira robot massager

If you want to receive or give a 6-arm massage, the option is the KIRA robot massager that comes with four specialized arms.
7. Laboratory automation
And it is that many repetitive actions are carried out in a health laboratory.
The Copenhagen University health laboratory was flooded with blood samples and required 3,000 tests a day. The team added 2 UR robots to their process, allowing them to achieve incredible productivity gains.
Analysis of how much robotic surgery costs
According to a report by the American Society of Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons ( Sages ) of the USA based in Los Angeles CA they noted:.
They find a significant increase in the Costs of general surgeries for their health system, when the robotic system is used instead of the traditional laparoscopy system.

It should be noted that their analysis does not include acquisition or maintenance costs, service contracts and training costs.
The result of their analysis is that unless a future study is carried out on whether a significant improvement in recovery in patients is found, they find that the benefit of the implementation does not go according to the costs , at least for them, for a limited budget like theirs.
Benefits
Robotics in healthcare brings numerous benefits that go beyond improving patient outcomes. They can also help establish more efficient processes in clinical settings, provide a safer work environment for healthcare workers, and improve the overall quality of patient care.
The great benefits of surgeries performed with these robotic technologies in the operating rooms, the results are usually shorter restoration times and less discomfort for the patient.
Conclusion
In conclusion, what this means is that medicine is undergoing strong changes that are directed towards medical robotics, with which they will be able to provide better and more precise diagnoses, safer and less invasive surgery with fewer infections and an increase in the rates of survival in very risky surgeries.
Although more comparative studies are needed in terms of costs, there is no price for health. And it is clearly that we will all be happy.
